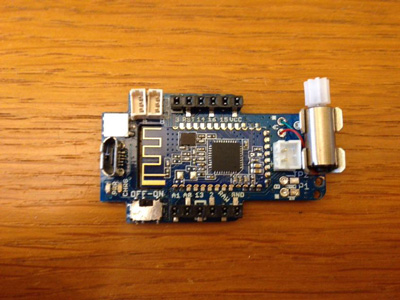
Coding guide
The 3DRacers Pilot control Board can be programmed with Arduino.
It supports a wide range of sensors and devices, SPI, I2C, other than the on-board devices. It can drive up to 2 Motors, 2 Micro Servos (plus other via other Pins)
Available pins includes: 8 Digital I/O, 2 PWM, 2 Analog IN, 4 High current (Motors)
Other sections
Documentation - App Guide - Online Editor - Assembly Guide - GitHub Sources
Quick Start
To start programming your 3DRacers, you’ll need Arduino IDE >= 1.6 and then:
- Download the 3DRacers hardware definition.
Unzip the archive in the
hardwarefolder of the Arduino IDEDownload the 3DRacers Library
Unzip the archive in the
librariesfolder of the Arduino IDEAlso copy the
Lib3DRacersVendorsfolder from the Archive in thelibrariesfolder
Restart the Arduino IDE and look at the Arduino Menu: File -> Examples -> Lib3DRacers.
Here you’ll find several example programs for the Pilot Board, like the easy sketch.
Anathomy of a 3DRacers Sketch
3DRacers
Easysketch:
#include <3DRacers_Vendors.h>
#include <3DRacers.h>
ThreeDRacers racer;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
racer.Begin(Serial1, Serial);
racer.OnDriveCommand(OnDriveCommand);
racer.OnConfigCommand(OnServoConfigCommand);
}
void loop() {
racer.Process();
}
void OnDriveCommand(DriveCommand& cmd, CarInfo& car)
{
//Motors:
int motorOutput = cmd.throttle;
if (cmd.brake) { racer.MotorBrake(); }
else if (cmd.reverse) { racer.MotorMoveBackwards(motorOutput); }
else if (cmd.throttle == 0) { racer.MotorStop(); }
else { racer.MotorMoveForward(motorOutput); }
//Steer:
racer.SetServo(cmd.steerAngle);
if(cmd.changeColor) { racer.LedColor(cmd.red, cmd.green, cmd.blue); }
}
void OnServoConfigCommand(ConfigCommand& cmd, CarInfo& car)
{
//Steer calibration:
if (cmd.flags.steerCenterChanged == true) {
racer.SetServoCenter(cmd.steerCenter);
}
if (cmd.flags.steerMaxChanged == true) {
racer.SetServoMaxAngle(cmd.steerMax);
}
}
The Easy example is a good start on learning the basics of the 3DRacers Library methods.
Includes
#include <3DRacers_Vendors.h>
#include <3DRacers.h>
To use the library simply include those two files. The 3DRacers_Vendors.h file will include the required dependecies for the library.
The Racer object
ThreeDRacers racer;
The racer object is the object that you’ll use to interface with the 3DRacers hardware.
Setup code
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
racer.Begin(Serial1, Serial);
racer.OnDriveCommand(OnDriveCommand);
racer.OnConfigCommand(OnServoConfigCommand);
}
In the setup code we start the Serial on your choice of baud rate, and pass it to the racer object
We can then pass two handle functions to the object.
OnDriveCommandwill be called when a command is sent from the smartphone appOnServoConfigCommandwill be called when a config command is issued from the app (ie: steering center and calibration)
Driving Command
In theOnDriveCommand you can see the basics methods used to control a 3DRacers: racer.MotorMoveForward, racer.SetServo, or racer.LedColor
void SetServo(int value); //value must be in the [-90, 90] range, will be automatically mapped to the actual steer range (NB: Hardware servo is 90° for center, range from to +-60)
void SetServoCenter(int value);
void SetServoMaxAngle(int value);
void MotorMoveForward(int speed);
void MotorMoveBackwards(int speed);
void MotorStop();
void MotorBrake();
void LedColor(byte red, byte green, byte blue);
//Use only for low level control, use Motor* functions if possible
void MotorControl(int controlSpeed, bool brake);
//CALLBACKS
//Set this callbacks to your functions to customize the bot behaviour:
void OnConnect(void(*f)(CarInfo&, ConfigCommand&)){ processConnectCommand = f; }
void OnDriveCommand(void(*f)(DriveCommand&, CarInfo&)){ processDriveCommand = f; }
void OnConfigCommand(void(*f)(ConfigCommand&, CarInfo&)){ processConfigCommand = f; }
void OnRaw1Command(void(*f)(void*, CarInfo&)){ processRaw1Command = f; }
void (*OnGateDetected)(CarInfo& car){}
//TX towards central device
void OnAckNotification();
For a full list of the available methods and callbacks see the 3DRacers.h file
The data packets
DriveCommand structure
The data sent from the App is contained in the DriveCommand structure.
DriveCommand structure:
struct __attribute__ ((packed)) DriveCommand
{
char id;
unsigned int packetCount;
byte crc;
short throttle;//From 0 to 1024 //2B
short steerAngle;//From -90 to 90 //2B
bool brake;
bool reverse;
byte red;
byte green;
byte blue;
bool changeColor;
}
CarInfo structure
While the CarInfo structure will hold the current status of the 3DRacers
CarInfo structure:
typedef struct CarInfo
{
//car info
int maxBatteryLevel;
int minBatteryLevel;
//drive state
short throttle;//From 0 to 1024
short steerAngle;//From -90 to 90
bool brake;
bool reverse;
}
Reference
SetServo
SetServo(int value) get a value from -90 to 90, and steer the car from the minimum to maximum steering angle allowed.
See SetServoMaxAngle for info on how to configure the maximum steering angle.
SetServoCenter
void SetServoCenter(int value) configure the central position of the steering. When usually 90°, it can be fine-tuned from the app or through the console.
Usefull when the car divert to a side.
SetServoMaxAngle
void SetServoMaxAngle(int value) configure the maximum steering angle allowed by the car chassis. It should be configured so that the Servo doesn’t clash to the plastic or emit a noise when going to the end of the movement range.
The 3DRacers servo motor has a steering range of +-60°, while usually the 3DRacers car chassis allows for a range of 30-35°.
MotorMoveForward
void MotorMoveForward(int speed) Move the primary motor forward with a speed from 0 to 255
MotorMoveBackwards
void MotorMoveBackwards(int speed) Move the primary motor backward with a speed from 0 to 255
MotorStop
void MotorStop() Stop the primary motor, while allowing it to freely spin.
MotorBrake
void MotorBrake(); Stop the primary motor and short-circuit the DC motor so that it will oppose to the movement.
LedColor
void LedColor(byte red, byte green, byte blue) Change the led color of the onboard RGB led
MotorControl
void MotorControl(int controlSpeed, bool brake) Directly interact with the Motor, use only for low level control, use Motor* functions if possible
//CALLBACKS
Callbacks
The following callbacks will be called after a certain event happens. You can pass a function to one of them to have it called.
The passed callback function must have the same signature of the callback. For eg:
Example for the
void OnDriveCommand(void(*f)(DriveCommand&, CarInfo&))callback:
void OnDriveCommand(DriveCommand& cmd, CarInfo& car)
{
//Your code here
}
racer.OnDriveCommand(OnDriveCommand);
OnConnect
void OnConnect(void(*f)(CarInfo&, ConfigCommand&)) Called when the smartphone app connected to the 3DRacers Pilot. Also on reconnect.
OnDriveCommand
void OnDriveCommand(void(*f)(DriveCommand&, CarInfo&)) Called when a drive packet is received, see also the DriveCommand structure.
OnConfigCommand
void OnConfigCommand(void(*f)(ConfigCommand&, CarInfo&)) Called when a config packet is received from the smartphone app, see also the ConfigCommand structure.
OnGateDetected
void (*OnGateDetected)(CarInfo& car) Called when a gate is detected from the IR sensor under the 3DRacers
OnRaw1Command
void OnRaw1Command(void(*f)(void*, CarInfo&)) Allows to define custom packet to send from the App to the 3DRacers board. Work in progress.
OnAckNotification
void OnAckNotification() Called when the 3DRacers Pilot board is about to send a packet back to the smartphone App. Used to define custom packets to send back to the App, during the Ack window, to avoid choking the app with too many packets that could slow down the driving packets.
Work in progress.
Tech Specs
ATMega32U4processor- Motor driver for 2 DC Motors
DRV8835 - Bluetooth Low Energy 4.1 radio
- LiPo battery charger
LM73831 - Drive 2 Servo, 2 DC Motors, 8 digital/analog IN/OUT Pins
- On board high efficency DC motor
- RGB Led
WS2812 - IR Gate sensor
- Programmable via USB
- Shield support:
Accelerometer/Gyro Shield,Proto Shield